What is Software-Defined WAN (or SD-WAN or SDWAN) ?
 SD-WAN Explained
SD-WAN Explained
SD-WAN is similar to Software-Defined networking in that is decouples the wide area network from the underlying transport network. Companies use SD-WAN to create a software-defined overlay network that is independent from the carrier or physical underlying network. This network overlay is often used to improve network performance and reliability. Additionally, because a Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) is independent of the underlying network, remote sites can quickly and easily be provisioned using the locally available bandwidth. Companies deploying an SD-WAN overlay typically see a significant decrease in the overall cost of the wide area network.
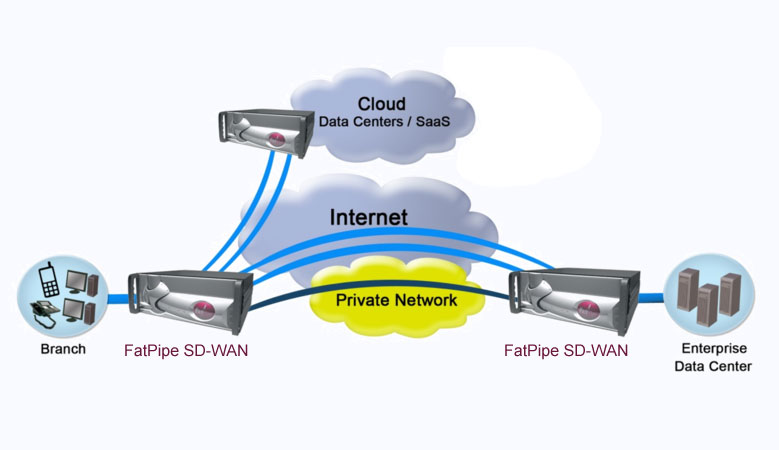
Multiple Connections
Take advantage of our virtual WAN architecture that optimizes any combination of multiple transport services.
Centralized Control
Ensure data security and decision driven traffic routing through a centralized control function with additional benefits such as application performance, user satisfaction, business efficiency and reduced operational expenditure.
Dynamic Path Selection
Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) intelligently prioritizes data and diagnoses existing network conditions to effectively map application traffic to the best suited route.
Policy-Based Management
Be it enhancing VoIP performance, reducing costs or optimizing security, SD-WAN dynamically translates your business' goals and objectives into policies for network management that are implemented across all gateways and routers.
Service Chaining
SD-WAN can be coupled with WAN Optimization to augment network and application deliverables while cloud based services can scrutinize internet traffic at branches based on security requirements.
Last Mile Connectivity
Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) devices deployed at each location augment last mile connectivity between sites without being excessively dependent on service partners, as is the case with cloud based solutions.
Cost Savings
Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) gives you the luxury of replacing expensive connections with limited bandwidth with more affordable connections with greater bandwidth.
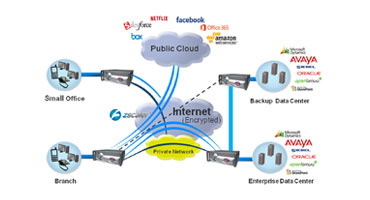
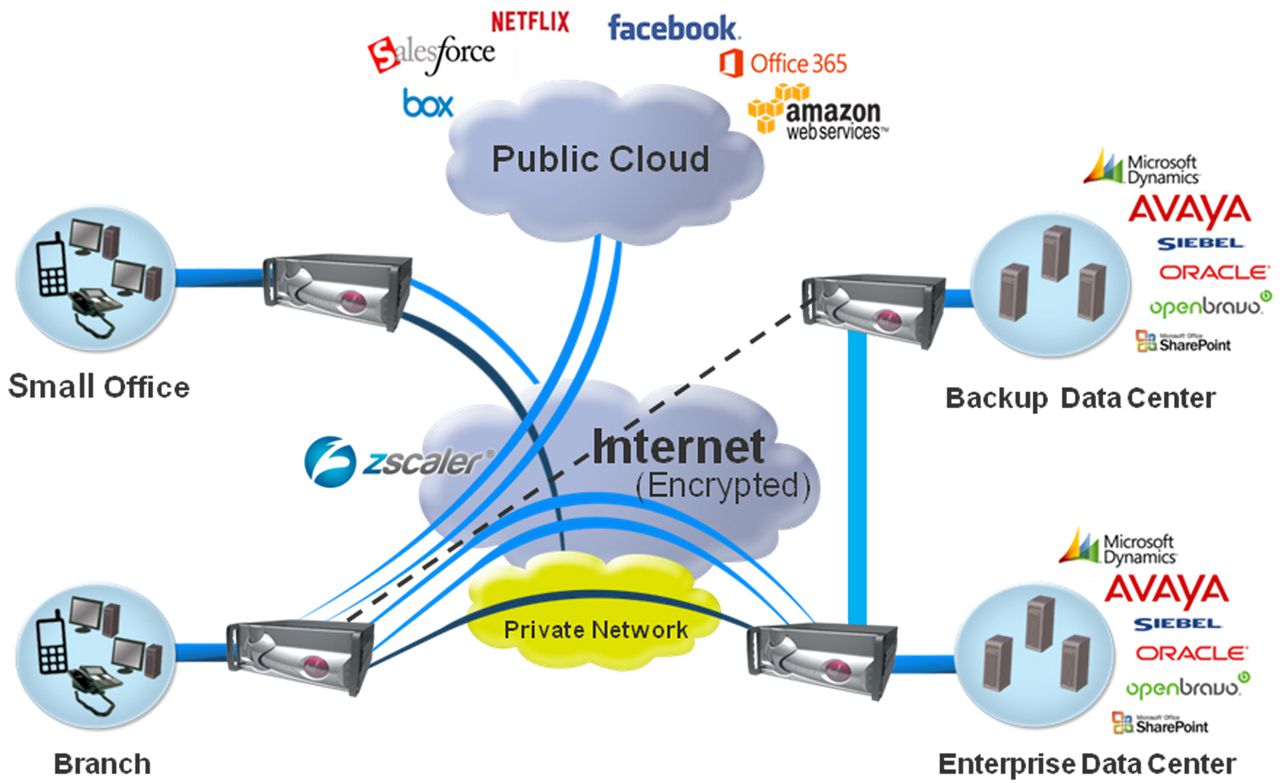
Migration from private to hybrid (public/private) network for branch connectivity
- Branch traffic can be routed back to the data center through private networks or IPSec VPNs before crossing over to the Internet so that networks can have a single, secure gateway
- All Internet traffic can be routed to a cloud based firewall, security hub or secure web gateway (SWG) before routing to the Internet, thereby reducing data center load while maintaining a single security parameter
- Traffic meant for specific, trusted sites is routed directly to those sites while other traffic is subjected to additional security, thereby reducing the load on the security device
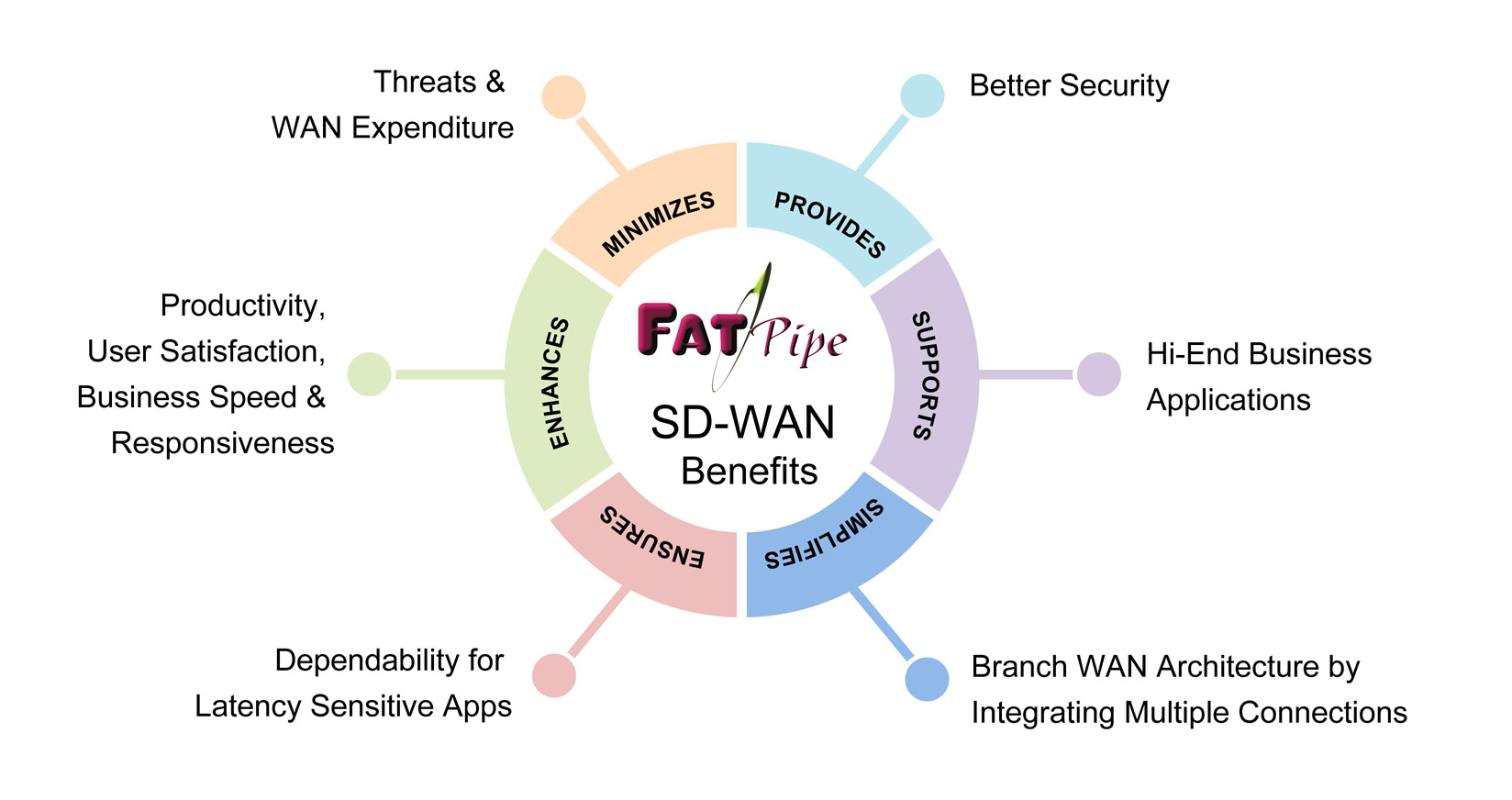
 What are the benefits of SD-WAN?
What are the benefits of SD-WAN?
SD-WAN eliminates the need to backhaul traffic for security screening with a design that's compatible with in-house data centers, public or private clouds, SaaS solutions and more.
You can leverage a cloud-first business model with SD-WAN. Traffic can be routed based on a variety of parameters such as priority, QoS and security, depending on business objectives. This can be done intelligently - for instance, through the internet, cloud based security service or main office based next generation firewall - depending on the mission criticality of various applications.
Direct internet access enhances SaaS and IaaS traffic, as well as the performance of other cloud applications locally protected by security measures at the branches.
SD-WAN's unified platform that consolidates various control functions lets you overcome the security, latency and performance limitations of broadband connections, especially those of mission critical operations while simplifying manageability regardless of the scale of operations.
Issues that can be resolved with SD-WAN
- Stalled branch deployments due to provisioning delays at a company's carrier
- 1 to 3 months for provisioning T1 connections from MPLS providers even after paying expedite fees
- Heavy reliance on VPN owing to lack of MPLS availability or high costs
- Conventional networking techniques that create single points of failure in the last mile
- Data transmissions through costly MPLS frameworks before reaching the Internet
Resolving Business Connectivity Issues with SD-WAN
MPLS Cost Constraints
SD-WAN lets you overcome MPLS cost constraints and cloud connectivity issues with inexpensive broadband connections. With a hybrid-WAN network design,
you can direct mission critical and secondary traffic across MPLS and broadband respectively.
Network Complexity
Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) simplifies network complexity through a combination of hybrid WAN designs and an increasingly cloud-centric solution. Systems can be adapted to changing business
needs while new equipment and gateways can be incorporated into remote sites from a central location. SD-WAN allows you to design and deploy business oriented policies
for efficient device management. Furthermore, devices are automatically aligned to existing policies when changed or modified.
Public Network Unpredictability
SD-WAN can adapt routing decisions based on real time public network diagnostics that detect latency, bandwidth constraints, bottlenecks and more. High priority traffic is transmitted across faster connections while less reliable links are reserved for less important data.
The benefits of SD-WAN become relevant in the case of:
- Remote locations using public and private WANs in an active-active setup
- Customer premise equipment in physical or virtual form factors that run on commodity hardware
- A secure, hybrid WAN architecture that dynamically manages traffic based on application policy, availability and so on
- Mission critical and real time applications where security and corporate governance and compliance policies define traffic visibility, prioritization and routing
- Hybrid WANs that facilitate high availability and resiliency
- L2 and L3 interoperability with directly connected routers and/or switches
- Central dashboard that provides insights into site, application and VPN performance
- Open north bound API for controller access and mgmt.: log events to net event co-relation mger, SIEM
- Zero touch deployment at branch location with negligible configuration changes on directly connected infrastructure
- FIPS 140-2 validation certification for cryptography
FatPipe Orchestrator
- Simplified WAN control & management for networks already overloaded with bandwidth heavy applications that use VoIP and video
- Growing bandwidth requirements don't match bandwidth cost reduction
- New "as-a-service" and cloud based application models have rendered conventional "star" or "hub & spoke" models inefficient
- More bandwidth with direct Internet access at branch locations
- Advanced policies for secure data transmissions to the cloud directly through local Internet connections
- Centralized management for zero-touch branch provisioning
- Open APIs for network integration